TL;DR
- What is MISRA? MISRA (Motor Industry Software Reliability Association) provides coding guidelines for developing safety-critical automotive software. Originally developed in 1998 for the UK automotive industry, MISRA has since grown to become the global standard for automotive software safety.
MISRA C compliance doesn’t require perfect adherence to every rule. After implementing MISRA across £500k+ of automotive projects, we’ve learned that much of the MISRA standard encompasses good software practices already, with a focus on 20% of the rules that provide enhanced safety benefit.
- Integrate MISRA checking as early as possible. Start with a risk-based approach for the Guideline Recategorisation Plan, use cost-effective toolchains during development (save expensive automotive tools for final certification), and prioritise memory management and control flow rules.
- Typical costs: £15-25k setup plus 15-25% development time increase, but ROI comes through 40-60% fewer field defects and faster customer approval processes.
Contents
MISRA C Compliance in Practice: A Design Engineer's Guide to Automotive Software Standards
When we started our first MISRA project for a Tier 1 automotive supplier, the client’s initial requirement seemed straightforward:
“Everything must be MISRA compliant.”
Six months later, we’d learned the reality is far more nuanced – and practical – than the standards suggest.
After implementing MISRA across eight concurrent automotive projects worth over £500,000, I’ve discovered that successful MISRA compliance isn’t about perfect adherence to every rule.
MISRA is actually about intelligent implementation that balances safety, cost, and delivery timelines.

What is MISRA in UK Automotive Software Development?
MISRA (Motor Industry Software Reliability Association) provides coding guidelines for developing safety-critical automotive software. Originally created in 1998 for the UK automotive industry, MISRA has evolved into the global standard for automotive software safety.However, there's a significant gap between MISRA theory and real-world implementation. Most automotive suppliers—particularly smaller UK firms—struggle with three fundamental challenges:
- Over-interpretation of requirements leading to unnecessary complexity
- Tool costs that can reach tens of thousands for compiler licences
- Legacy code integration where full compliance isn't practically achievable
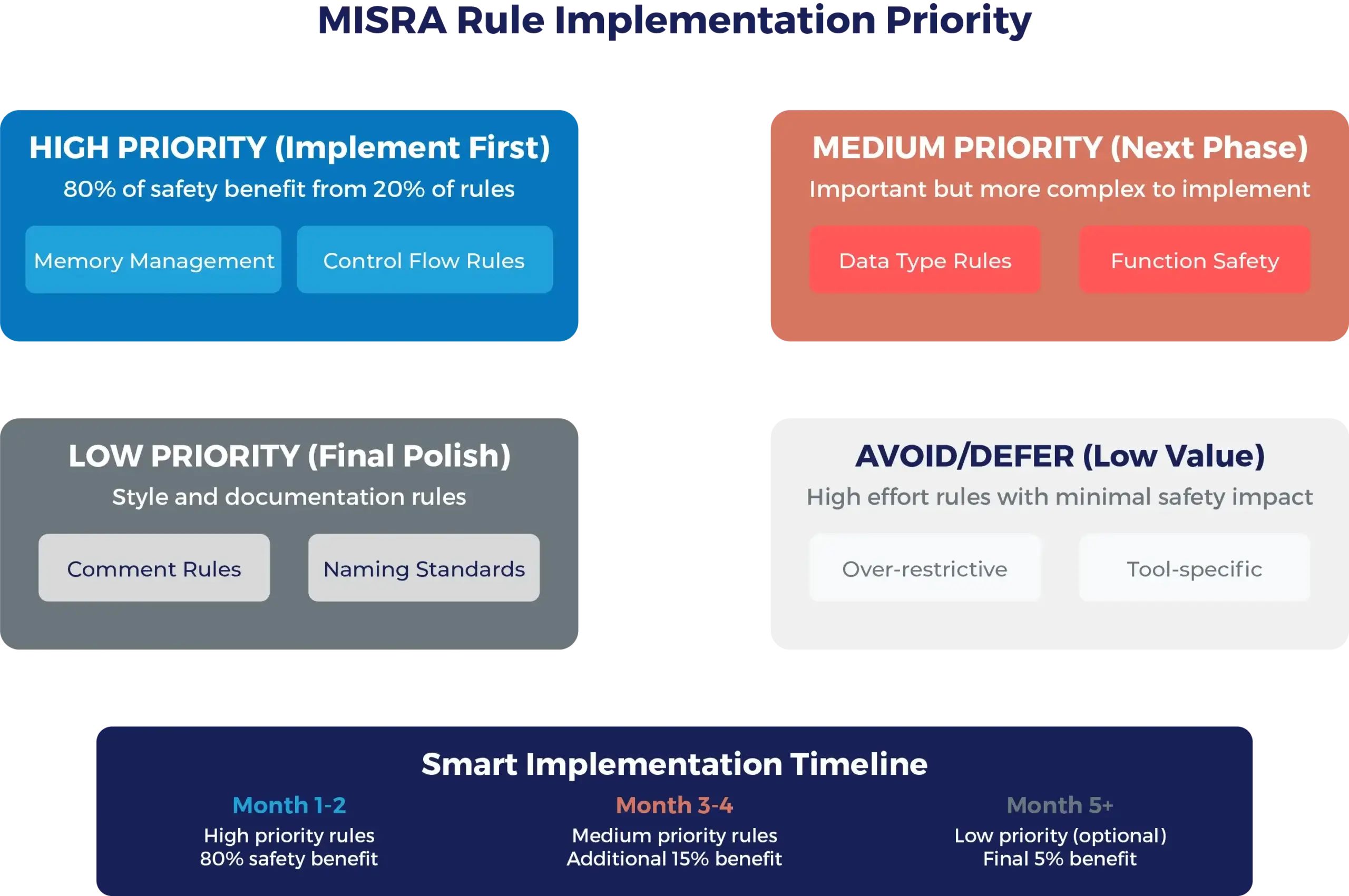
The 80/20 Principle of MISRA Implementation
Working with automotive Tier 1 suppliers has taught us that pragmatic compliance often trumps perfect compliance.
In practice, 20% of MISRA rules go beyond standard good practice to provide 80% of the safety benefit.
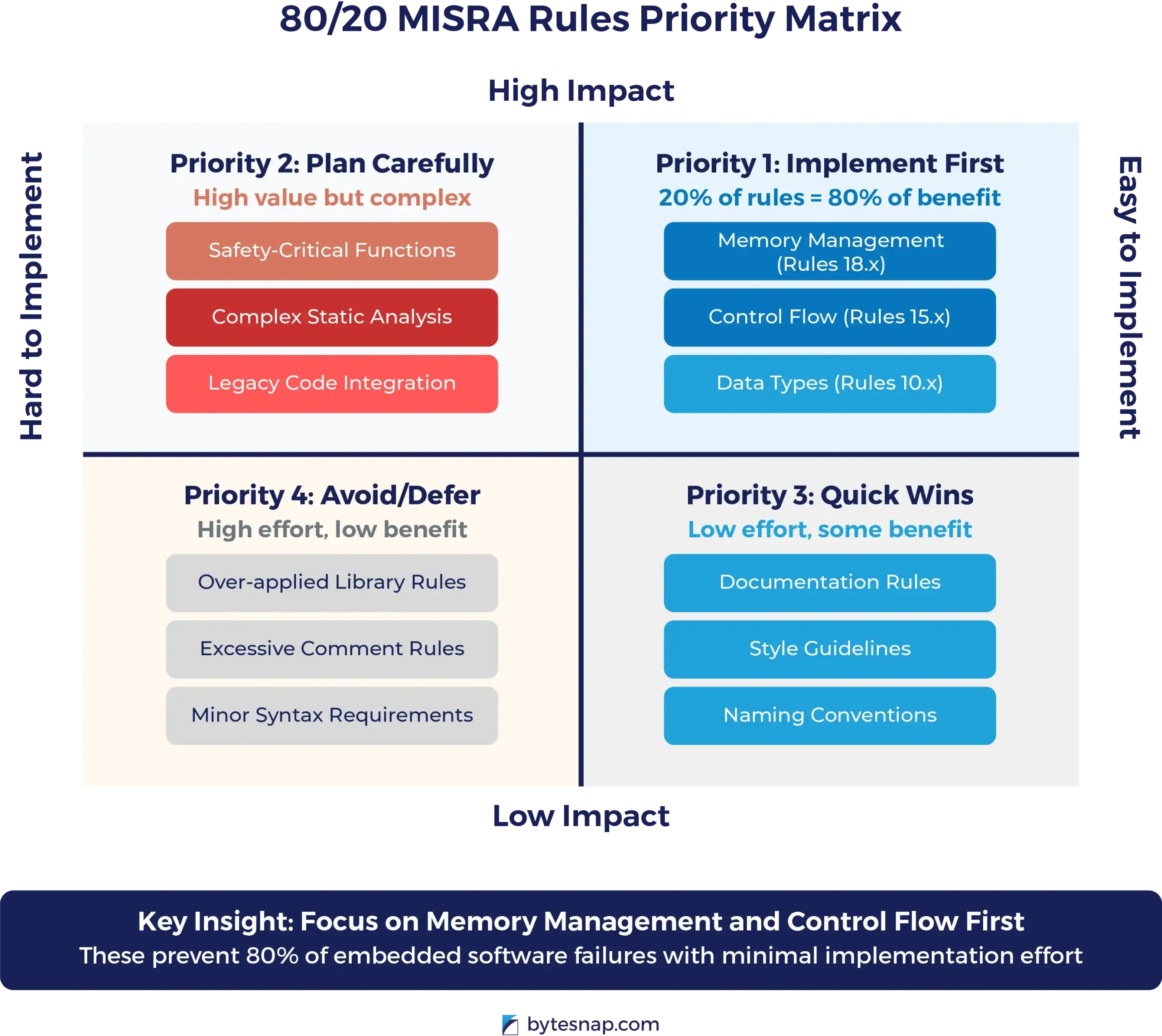
MISRA Rules That Matter Most
Memory Management (Rules 18.1-18.8)
These rules prevent buffer overflows and memory corruption—the most common causes of automotive software failures.
// MISRA Rule 18.1 - Prevent array bounds violations
uint8_t sensor_data[MAX_SENSORS];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_SENSORS; i++) {
// Safe array access within bounds
process_sensor(sensor_data[i]);
}
Control Flow (Rules 15.1-15.7)
Ensuring predictable program behaviour under all conditions.
Data Types (Rules 10.1-10.8)
Preventing implicit conversions that can cause unexpected behaviour.
Which MISRA Rule Is Often Over-Applied?
MISRA Rule 21.x (Standard Library Functions).
This rule often gets taken too far in automotive projects, with some teams banning all standard library functions when a bit of common sense and clear reasoning would do the trick.
The key is to avoid blanket bans; instead, go with thoughtful, case-by-case decisions to make compliance less restrictive and more effective for your project goals.
UK Automotive MISRA Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Requirements Analysis and Risk Assessment
Understanding Your Client’s Actual Needs
Most automotive suppliers request “full MISRA compliance” when they actually need “safety-critical compliance for customer-facing modules.”
We’ve found that breaking down requirements by system criticality saves 30-40% of implementation effort.
Risk-Based Rule Selection Framework:
- Safety-critical modules: Apply all relevant MISRA rules
- Non-critical support functions: Focus on memory management and control flow rules
- Legacy integration points: Document deviations with technical justification
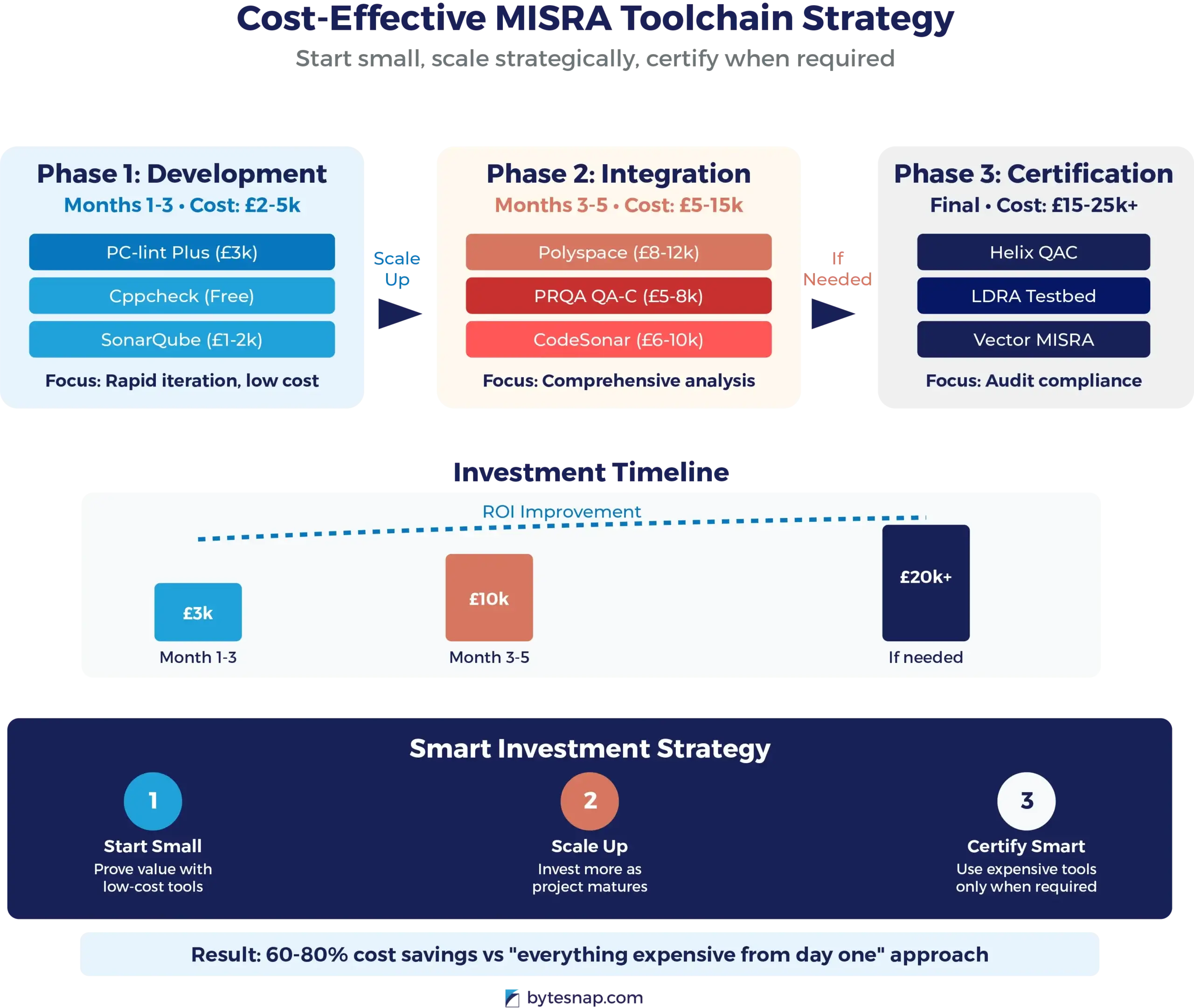
Phase 2: Cost-Effective Toolchain Selection
Beyond Expensive Automotive Compilers
Whilst automotive-grade compilers cost £20,000+, effective MISRA compliance doesn’t require the most expensive tools for every project phase.
Recommended Toolchain Approach:
- Development phase: Open-source MISRA checkers (PC-lint Plus, Cppcheck)
- Integration testing: Mid-range commercial tools (£2,000-5,000)
- Final certification: Automotive-grade tools (when customer-mandated)
Tool Selection Criteria:
- Rule coverage matching your selected MISRA subset
- Integration with existing development workflows
- Cost-effectiveness for project scale
- UK supplier support and training availability
Phase 3: Practical Team Training
Recommended Toolchain Approach:
Standard MISRA training focuses on rule memorisation. However, effective automotive software development requires practical application skills.
MISRA Training Approach at ByteSnap Design:
- Rule rationale workshops: Understanding why rules exist
- Real codebase reviews: Applying MISRA to actual automotive projects
- Deviation justification training: Documenting pragmatic decisions
- Tool-specific implementation: Hands-on experience with selected checkers
What are the Most Common Pitfalls when Implementing MISRA?
Pitfall 1: Over-Compliance Without Business Justification
The Problem: Implementing every MISRA rule regardless of system criticality or customer requirements.
Our Solution: Risk-based compliance where rule selection matches safety requirements. For instance, a door controller doesn't need the same compliance level as an engine management system.
Pitfall 2: Tool Dependency Without Skills Development
The Problem: Relying entirely on expensive tools without understanding the underlying safety principles.
Our Solution: Combine automated checking with manual code reviews. Tools catch syntax violations; experienced engineers identify safety-critical logic issues.
Pitfall 3: Documentation Overhead That Stifles Productivity
The Problem: Creating excessive documentation for every minor deviation.
Our Solution: Standardised deviation templates focusing on safety impact and technical justification.
Legacy Code Integration Strategies: Working with Existing Automotive Codebases
Most UK automotive software projects involve integrating MISRA compliance with existing code that predates the standards. Complete refactoring isn’t always feasible or cost-effective.
Practical Integration Approach
Baseline Assessment:
Identify safety-critical modules requiring full compliance
Categorise existing code by modification feasibility
- Establish compliance targets by module importanc
Incremental Compliance Strategy
Apply MISRA rules to all new code development
Gradually refactor high-impact legacy modules
Document justified deviations for stable, low-risk code
Incremental Compliance Strategy
Create MISRA-compliant wrapper functions for non-compliant legacy code
Implement input validation at all legacy interface points
Maintain clear separation between compliant and non-compliant modules
ROI and Business Case for MISRA Implementation:
Cost-Benefit Analysis for UK Automotive Suppliers
Implementation Costs (Typical Mid-Size Project):
- Training and tool setup: £15,000-25,000
- Development overhead: 15-25% increase in coding time
- Documentation and review processes: £8,000-12,000
Business Benefits:
- Reduced warranty claims: 40-60% fewer field defects
- Faster certification: Streamlined automotive qualification
- Customer confidence: Demonstrable commitment to safety
- Market differentiation: Competitive advantage for new business
Time-to-Market Considerations:
Contrary to common perceptions, well-implemented MISRA compliance can actually accelerate time-to-market through:
- Reduced warranty claims: 40-60% fewer field defects
- Faster certification: Streamlined automotive qualification
- Customer confidence: Demonstrable commitment to safety
- Market differentiation: Competitive advantage for new business
MISRA Compliance for Different Automotive Systems
Highest compliance requirements due to safety-critical nature and emissions regulations.
Key Focus Areas:
- Real-time constraints and timing predictability
- Sensor data validation and range checking
- Fail-safe behaviour implementation
- ISO 26262 functional safety integration
Moderate compliance requirements with emphasis on robustness rather than safety-critical behaviour.
Practical Approach:
- Focus on memory management and data integrity
- Implement graceful degradation for non-critical failures
- Prioritise user experience over perfect compliance
Selective compliance focusing on security and data protection rather than traditional safety requirements.
Modern Considerations:
- Cybersecurity implications of connected systems
- Data privacy requirements under UK GDPR
- Integration with non-automotive software ecosystems
UK Automotive Software Development Advantages:
Why Location Matters for MISRA Implementation
Direct Communication Benefits
Time Zone Alignment
Regulatory Understanding
Choosing the Right MISRA Implementation Partner:
Red Flags to Avoid
Tool Vendors Masquerading as Consultants
Theoretical Experts Without Practical Experience
Pushes One-Size-Fits-All Approach
Questions to Ask Potential Partners
Technical Competence
- “How many automotive MISRA projects have you completed in the last two years?”
- “Can you provide examples of pragmatic MISRA implementations with justified deviations?”
- “What’s your approach to legacy code integration?”
- “What are the total costs beyond daily rates?”
- “How do you handle scope changes and additional compliance requirements?”
- “What tools and licences are included in your quoted price?”
Advanced MISRA Implementation Techniques - Automated Compliance Monitoring
Continuous Integration Approaches Integrate MISRA checking into your build pipeline to catch violations early in the development cycle.
Custom Rule Configuration Tailor MISRA rule sets to your specific automotive application rather than applying generic automotive profiles.
Metric-Driven Improvement Track compliance metrics over time to identify recurring issues and training opportunities.
Team-Based Compliance Strategies
Peer Review Processes Implement structured code reviews focusing on MISRA compliance and safety implications.
Knowledge Sharing Frameworks Establish internal expertise sharing to reduce dependency on external consultants.
Gradual Skills Development Build internal MISRA expertise through mentored project work rather than theoretical training alone.
Future-Proofing Your MISRA Strategy
Emerging Automotive Technologies
Electric Vehicle Software Requirements MISRA compliance for EV systems introduces new considerations around high-voltage safety and battery management.
Autonomous Driving Software Higher levels of automotive autonomy will require enhanced MISRA compliance with ISO 26262 ASIL-D requirements.
Connected Vehicle Cybersecurity Integration of cybersecurity requirements with traditional MISRA safety standards becomes increasingly important.
Evolving MISRA Standards
MISRA C:2025 Updates The latest MISRA release introduces new guidelines while rationalising existing rules for better practical application.
Industry-Specific Adaptations Automotive OEMs are developing MISRA adaptations specific to their internal safety requirements and development processes.
Conclusion: Practical MISRA Implementation for UK Automotive Success
Effective MISRA compliance isn’t about sticking perfectly to every rule; it’s about intelligent implementation that balances safety, cost, and delivery timelines.
UK automotive software suppliers have unique advantages in language, time zones, and regulatory understanding that can be leveraged for competitive differentiation.
The key to successful MISRA implementation lies in:
Risk-based rule selection matching safety requirements to system criticality
Cost-effective toolchain choices appropriate to project scale and budget
Practical team training focused on real-world application rather than theoretical knowledge
Pragmatic legacy integration with properly documented deviations
After implementing MISRA across numerous automotive projects, we’ve learnt that the most successful approaches combine technical rigour with commercial pragmatism.
Ultimately, the goal isn’t perfect compliance; it’s safe, reliable automotive software delivered on time and within budget.
MISRA compliance expertise for your automotive project

Anthony is a Birmingham-based electronics and software engineer who has been creating bespoke embedded products since 2019.
While studying for his Masters in Electronics Engineering in 2018, he worked at the Aston Institute of Photonic Technologies, developing advanced laser control solutions for the in-house research teams. Since moving to ByteSnap, he has developed a wide range of products, from smartwatches and AI cameras to fluid monitoring and hydraulic control systems.
Outside of the office, Anthony enjoys creating digital art and snowboarding.





